Page Card
Filters
Belongs to subject Filters
Filtering is the process of reducing or eliminating the amplitude of selected frequencies in the spectrum of a sound signal. Filtering is one of the most important electronic music tools. We use filters to shape sounds, to bring out new colors, and to balance sounds together.
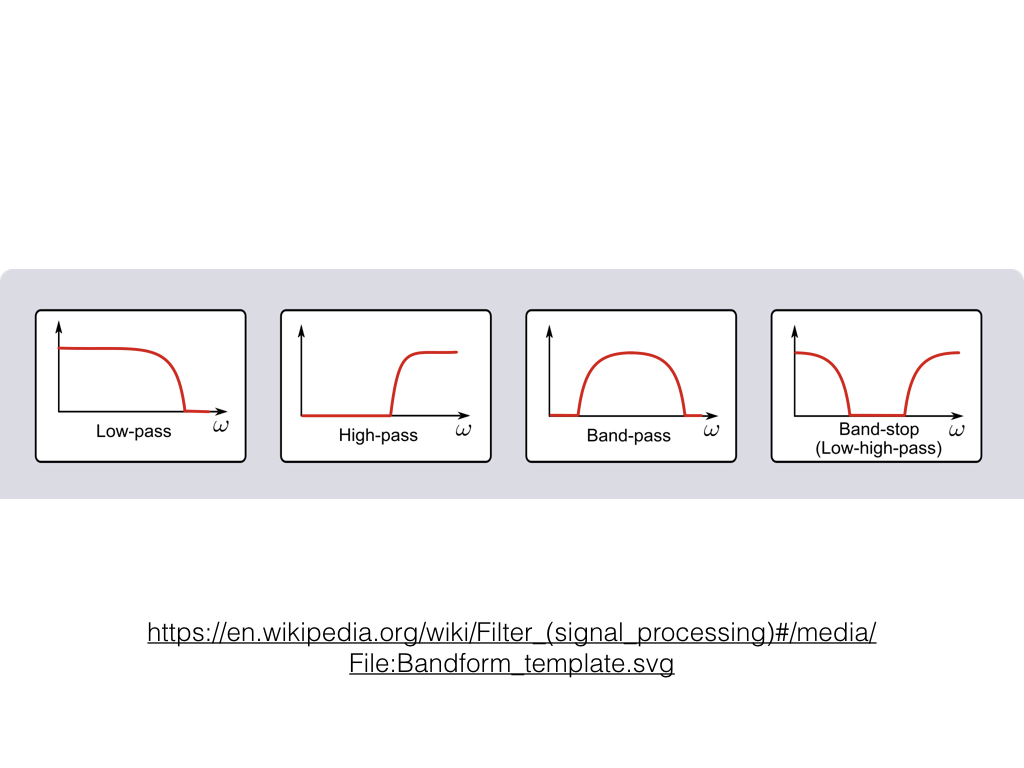
Types of Filters
The four main types of filters are low-pass, high-pass, band-reject, and band-pass. A low-pass filter reduces or eliminates high-frequency content. A high-pass filter reduces or eliminates low-frequency content. A band-reject filter reduces or eliminates content within a specific frequency range. A band-pass filter reduces or eliminates content outside of a specific frequency range. There are many types of filters, these are the four most common categories. We can describe most other filters by these four types of filters.
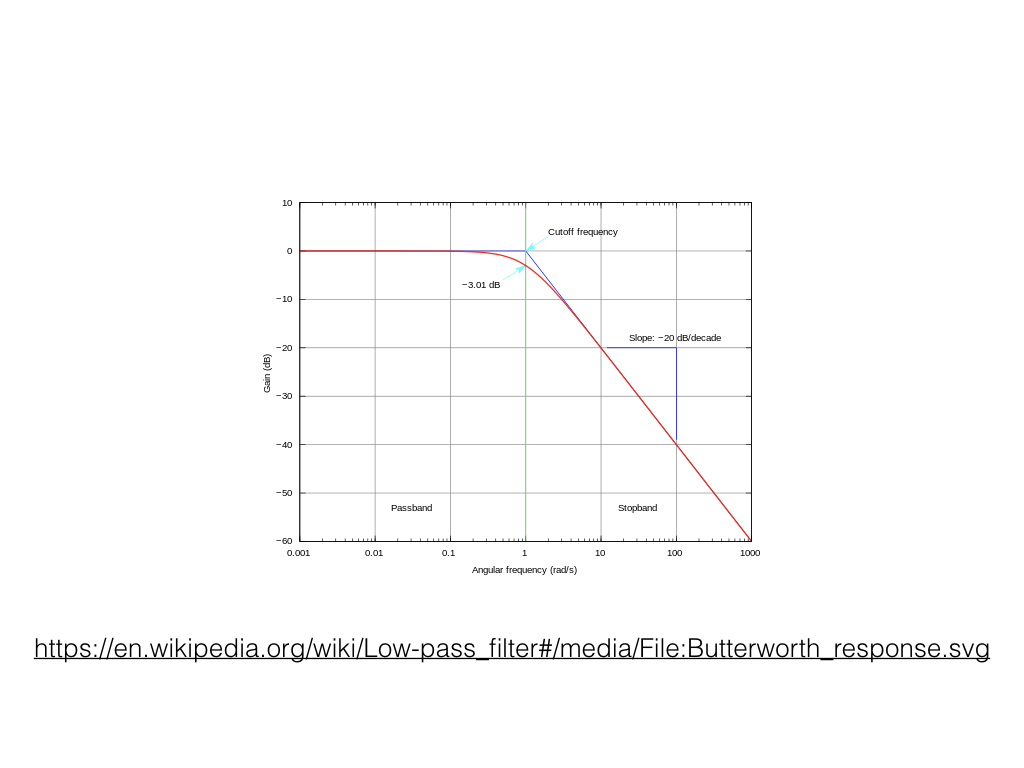
Filter Parameters
A filter typically has three parameters. The first is cutoff, which is the frequency or frequencies where the filtering will begin to occur. The gain is the amount of amplitude that we will impact. In some filters, if there's no gain parameters then the filter is removing the other content. Finally, the third common parameter we call "q", "slope", or "bandwidth". This parameter determines how smooth the transition is from unfiltered to filtered content.

In a System
Filters are often combined with other filters and sound effects. Remember that while you can make a filter with set properties, it is also possible to change these parameters over time. For example, a delay effect may apply filtering to the delayed copies of the sound source. Filtering is the most common sound changing technique we use in electronic music.